Nowadays, China has become the most active region for the development of machine vision in the world, with applications covering various industries of the national economy such as industry, agriculture, medicine, military, aerospace, and meteorology. Although the growth rate of machine vision is very fast, there are still many people who are not familiar with machine vision. Today, let's learn about machine vision.
Machine vision is the use of machines instead of human eyes for measurement and judgment. Machine vision system refers to the use of machine vision products (i.e. image capture devices, divided into CMOS and CCD) to convert the captured target into an image signal, which is transmitted to a dedicated image processing system. Based on pixel distribution, brightness, color and other information, it is transformed into a digital signal; The image system performs various operations on these signals to extract the features of the target, and then controls the equipment actions on site based on the discrimination results.
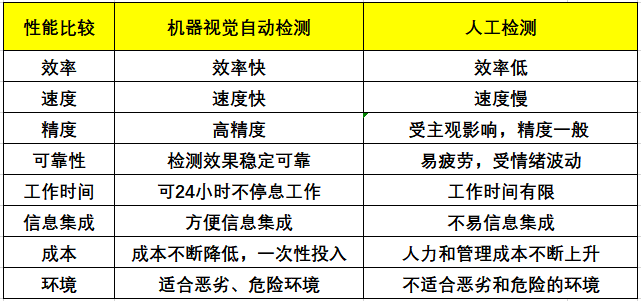
The advantages of machine vision
Machine vision systems have the characteristics of high efficiency and high automation, which can achieve high resolution accuracy and speed. The machine vision system has no contact with the detected object, ensuring safety and reliability. The main differences between manual detection and machine vision automatic detection are:
system composition
A typical machine vision system includes the following parts:
1. Lighting
Lighting is an important factor affecting the input of machine vision systems, which directly affects the quality of input data and application effectiveness. Due to the lack of universal machine vision lighting equipment, for each specific application instance, it is necessary to select the corresponding lighting device to achieve the best effect.
Light sources can be divided into visible light and invisible light. Common types of visible light sources include incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, mercury lamps, and sodium lamps. The disadvantage of visible light is the instability of light energy. So how to maintain the stability of light energy to a certain extent is an urgent problem that needs to be solved at present; On the other hand, ambient light may affect the quality of the image, so adding a protective screen can be used to reduce the impact of ambient light.
The lighting system can be divided into backlit, forward lit, structured light, and strobe lighting according to the illumination method. Among them, backlit illumination refers to the placement of the measured object between the light source and the camera, and its advantage is that it can obtain high contrast images; Forward lighting refers to the placement of the light source and camera on the same side of the object being measured, which facilitates installation; Structured light illumination is the process of projecting gratings or light sources onto the object being measured, and adjusting the three-dimensional information of the object based on their generated energy. Frequency flash lighting is the process of illuminating objects with high-frequency light pulses, and the camera requires synchronization with the light source.
2. Lens
Industrial lens
FOV (Field Of vision)=required resolution * sub-pixel * camera size/PRTM (part measurement tolerance)
When selecting a lens, attention should be paid to:
① Focal length
② Target height
③ Image height
④ Magnification factor
⑤ Distance from image to target
⑥ Center point/node
⑦ Distortion
3. Camera
According to different standards, it can be divided into standard resolution digital cameras and analog cameras, etc. Choose different cameras and high-resolution cameras according to different practical applications: line scanning CCD and area array CCD, monochromatic camera and color camera.
4. Image acquisition card
The image capture card is just a component of a complete machine vision system, but it plays a very important role; The image acquisition card directly determines the interface of the camera: black and white, color, analog, digital, etc.
A typical example is a PCI or AGP compatible capture card that can quickly transfer images to computer memory for processing. Some capture cards have built-in multiplexer switches. For example, you can connect 8 different cameras and tell the capture card which camera to use to capture the information. Some capture cards have built-in digital inputs to trigger capture, and when the capture card captures an image, the digital output port triggers a gate.
5. Visual processor
The visual processor integrates the acquisition card and processor. In the past, when computers were slow, visual processors were used to speed up visual processing tasks. Now, due to the fact that capture cards can quickly transfer images to memory and computers are much faster, visual processors are used less.
Industrial lens
1. Interface for industrial lenses:
Type C: The distance from the contact surface between the C-type interface lens and the camera to the focal plane of the lens (the position of the camera CCD photoelectric sensor) is 17.5mm
CS type: The CS type interface distance is 12.5mm, and the CS type lens can be used in conjunction with the CS type camera. Adding a 5mm C/CS adapter ring between the C-type lens and the CS type camera can be used in conjunction, but the CS type lens cannot be used in conjunction with the C-type camera.
F-type: Universal interface, generally suitable for lenses with a focal length greater than 25mm.
Basic parameters
Field of view: FOV, also known as field of view, refers to the visible range of the observed object, which is the part of the object that is filled with the camera acquisition chip.
Working distance, also known as WD, refers to the distance from the front of the lens to the detected object, which is the surface distance for clear imaging.
Resolution: The minimum resolution feature size that an image system can measure on the inspected object, and in most cases, the smaller the field of view, the better the resolution.
Depth of field: also known as DOF, the ability of a lens to maintain the desired resolution when an object is closer or farther from the optimal focus.
Focal length (f): It is a measure of the concentration or divergence of light in an optical system, referring to the distance from the center of the lens to the focal point of light focus. It is also the distance in a camera from the center of the lens to the imaging plane such as the lens or CCD.
The influence of focal length size: the smaller the focal length, the greater the depth of field; The smaller the focal length, the greater the distortion; The smaller the focal length, the more severe the gradual halo phenomenon, resulting in a decrease in illumination at the edge of the aberration.
Distortion: also known as distortion, refers to the main axis straight line in the plane of the subject that changes into a curve after being imaged by an optical system. The imaging error of this optical system is called distortion, and the distorted aberration only affects the geometric shape of the image, but does not affect the clarity of the image.
Aperture and F-value: Aperture is a device used to control the luminous flux of a lens, usually located inside the lens. We use F-values to express the aperture size, such as f2 and f4.
Key points for selecting industrial cameras
1. Field of view, optical magnification, and expected working distance: When selecting a lens, we will choose a lens slightly larger than the measured object's field of view, which is beneficial for motion control.
2. Depth of field requirements: For projects that require depth of field, use a small aperture as much as possible; When selecting lenses with magnification, try to use low magnification lenses as much as possible under project permission; If the project requirements are quite strict, it is preferred to choose a high depth of field sharp lens.
3. Chip size and camera interface: For example, a 2/3 lens supports a maximum industrial camera rake face of 2/3, but it cannot support industrial cameras larger than 1 inch.
4. Pay attention to the coordination with the light source and choose a suitable lens.
5. Installation space: It is not realistic for customers to change the device size when there are options available.
The working principle of machine vision
The machine vision detection system uses a CCD camera to convert the detected target into an image signal, which is transmitted to a dedicated image processing system. Based on pixel distribution, brightness, color, and other information, it is transformed into a digital signal. The image processing system performs various operations on these signals to collect the characteristics of the target, such as area, quantity, position, length, and then outputs results according to preset tolerance and other conditions, including size, angle, number, qualified/unqualified, with/without, etc., to achieve automatic recognition function.

Characteristics of Machine Vision
1. The camera's shooting speed automatically matches the speed of the object being measured, capturing the desired image;
2. The size range of the parts is 2.4mm to 12mm, and the thickness can vary;
3. The system selects workpieces of different sizes based on the operator's selection, calls the corresponding visual program for size detection, and outputs the results;
4. For parts of different sizes, sorting and conveying devices can accurately adjust the width of the material path, allowing the parts to move along a fixed path and undergo visual inspection;
5. The resolution of the machine vision system can reach 2448 × 2048, and the dynamic detection accuracy can reach 0.02mm;
6. The missed detection rate of waste products is 0;
7. This system can monitor the detection process by displaying images, and can also dynamically view the detection results through the detection data displayed on the interface;
8. It has the function of timely and accurately sending out removal control signals and removing scrap for incorrect workpieces;
9. The system can self check whether the status of its main equipment is normal, equipped with status indicator lights; At the same time, it is possible to set different operation permissions for system maintenance personnel and users;
10. Real time display of detection screen, Chinese interface, able to browse images of non-conforming products several times, with the function of storing and viewing incorrect workpiece images in real time;
11. The error result information file should include the corresponding error image and be able to print out.
The application fields of machine vision
1. Identification
2. Decoding of standard one-dimensional and two-dimensional codes
3. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and Confirmation (OCV)
4. Detection
5. Color and defect detection
6. Whether there is inspection of parts or components
7. Target position and direction detection and measurement
8. Size and capacity testing
9. Measurement of preset markers, such as the distance from hole position to hole position
10. Robot guidance
11. Output spatial coordinates to guide the precise positioning of the robotic arm
Disclaimer: Part of the content is sourced from the internet and is for the purpose of readers' learning and communication only. The copyright of the article belongs to the original author. If there are any issues, please contact for deletion.











